Suprane (desflurane)
The fast-acting anesthetic agent with low solubility1,2 in blood and tissues designed to help facilitate precise intraoperative control and rapid recovery.3,4

Having the lowest solubility of all anesthetic gases, Suprane (desflurane) offers fast wash-in and wash-out, swift control during surgery, and a rapid recovery for your patients.1,5 These features effectively make Suprane suitable for a wide range of patients and procedures, and particularly useful for patients in need of a fast recovery and earlier discharge from the hospital.

Meeting unique patient needs is critical for anesthesia recovery
We know that all patients are not the same. Changes in medical practice around surgeries mean that anesthesiologists need options for the optimal drug for each unique patient.
With populations of elderly patients growing, the predominance of obese patients increasing, the move to efficient same-day and ambulatory surgeries, and the implementation of ERAS protocols – anesthesiologists need a wide variety of options for induction, maintenance, and recovery from anesthesia.1,5
Video testimonials
Anesthesiologist, Central Military Hospital
Mexico City, Mexico
Video testimonials
Head of Anesthesia, Voivodship Hospital
Wloclawek City, Poland
Video testimonials
Anesthesiologist, Medical University Hospital
Łódź, Poland

Anesthetic agents with low solubility play an important role in recovery
In at-risk patient groups, like elderly and obese patients, as well as for procedures like neurosurgery, pulmonary surgery and cholecystectomy, precise intraoperative control and rapid recovery is desired. This can be achieved by using fast-acting anesthetic agents with a low solubility in blood and tissues.1, 6-10

Suprane’s low solubility results in precise control and fast, early recovery
Suprane has low blood and tissue solubilities. Its blood: gas partition coefficient is like that of nitrous oxide, and lower than that of sevoflurane and especially isoflurane. Suprane’s solubility in tissue is lower than for all the current halogenated inhaled anesthetic agents.1,11,19
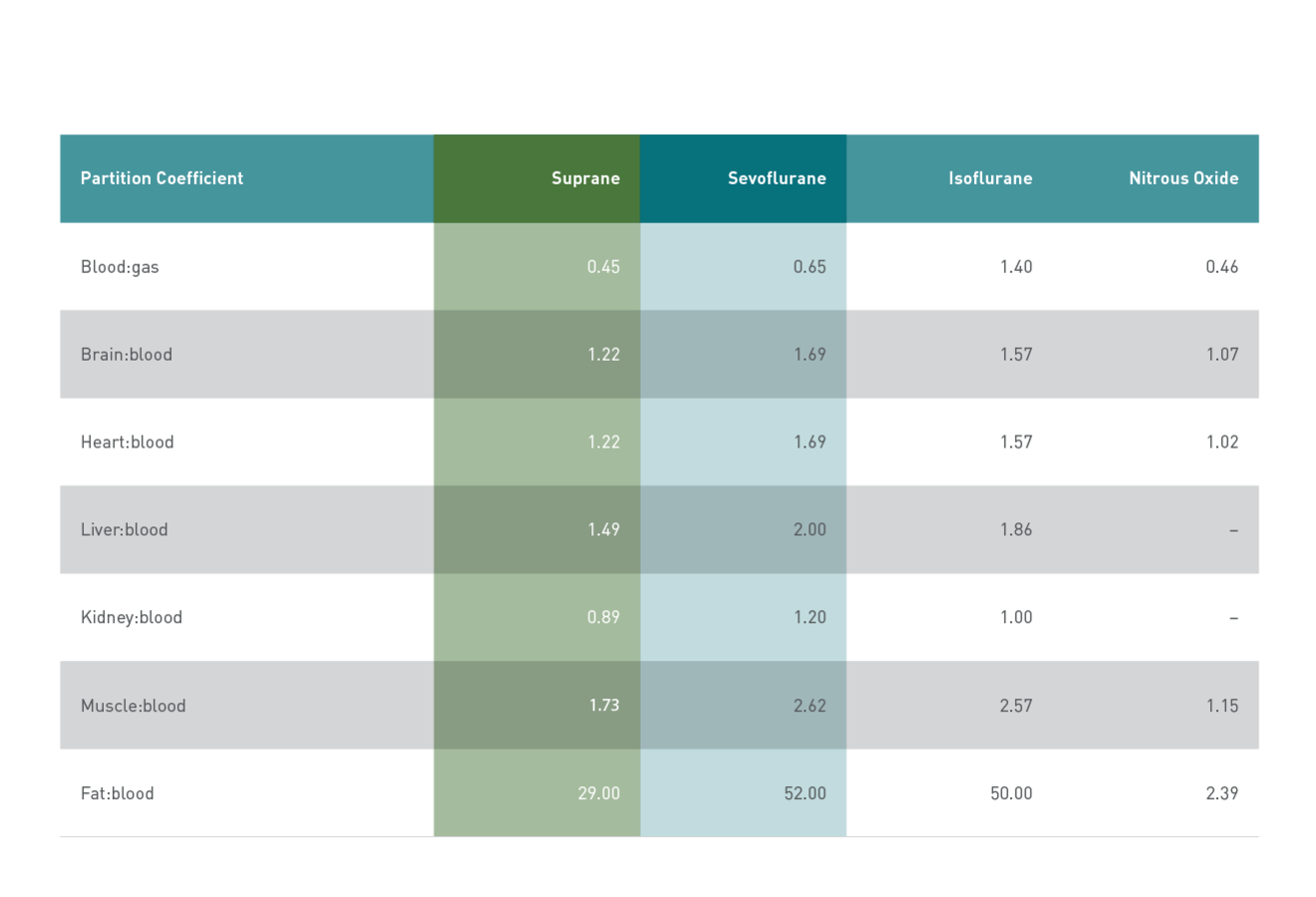
Partition coefficients of potent inhaled anesthetic agents
These favorable kinetic properties drive Suprane’s fast onset and offset and make it useful for precise control over acute, intraoperative changes in blood pressure and heart rate.5
After surgery, Suprane’s low solubility helps ensure an early and predictable recovery, making Suprane an optimal choice for post-anesthesia care. Rapid emergence and favorable recovery have been demonstrated across a wide range of patients and surgical interventions.7, 12-17

Suprane’s low fat blood partition coefficient makes it suitable for patients living with obesity
Suprane offers advantages in obese patients as compared to Sevoflurane, isoflurane and propofol with the lowest fat:blood partition coefficient and the lowest accumulation in fat tissue among current potent inhalational Anesthetics,6,20 it delivers a fast return of protective breathing reflexes as compared to sevoflurane, regardless of BMI6 and indicates a fast recovery in obese patients undergoing major abdominal surgery.20
See full prescribing information
Experience the benefits of Suprane in elderly patients for a faster and more predictable recovery than Sevoflurane
In elderly patients, Suprane provides a faster, clear-headed, and more predictable recovery, as compared with sevoflurane.8, 21 Its low lipid solubility and protective effects of volatile anesthetics after cardiac surgery may be an advantage for elderly patients.8
See full prescribing information
Use Suprane for patients undergoing neurosurgery or spinal surgery for quality recovery, as compared to Sevoflurane
The fast intraoperative and postoperative awakening times make Suprane suited for neurosurgery, including spinal surgery23, and enable early postoperative neurologic examinations.9,24 Through fast emergence time6,27 and quality recovery,26, 27-29 Suprane is highly applicable for patients with laryngeal mask airway (LMA), who also may benefit from a rapid return to protective airway reflexes after Suprane.6,25
*Suprane is not approved for maintenance of anesthesia in non-intubated children. Caution should be exercised when used for maintenance anesthesia with LMA or face mask in children 6 years old or younger.
See full prescribing information
Patients undergoing cholecystectomy or pulmonary surgery may benefit from rapid emergence as seen with Suprane
Patients undergoing cholecystectomy or pulmonary surgery benefit from a rapid emergence after Suprane, allowing for rapid extubation.10, 30
See full prescribing information
Suprane may have benefits during Cardiac Surgery
Like other volatile anesthetics, Suprane has been shown to protect the heart in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.18 In a meta-analysis review in cardiac surgery, general anesthesia with volatile anesthetics was associated with reduced long-term mortality, when comparing with TIVA.31
See full prescribing informationIn a study of maintenance anaesthesia in 60 patients undergoing short day-case gynaecological surgery12
Faster full ambulant recovery
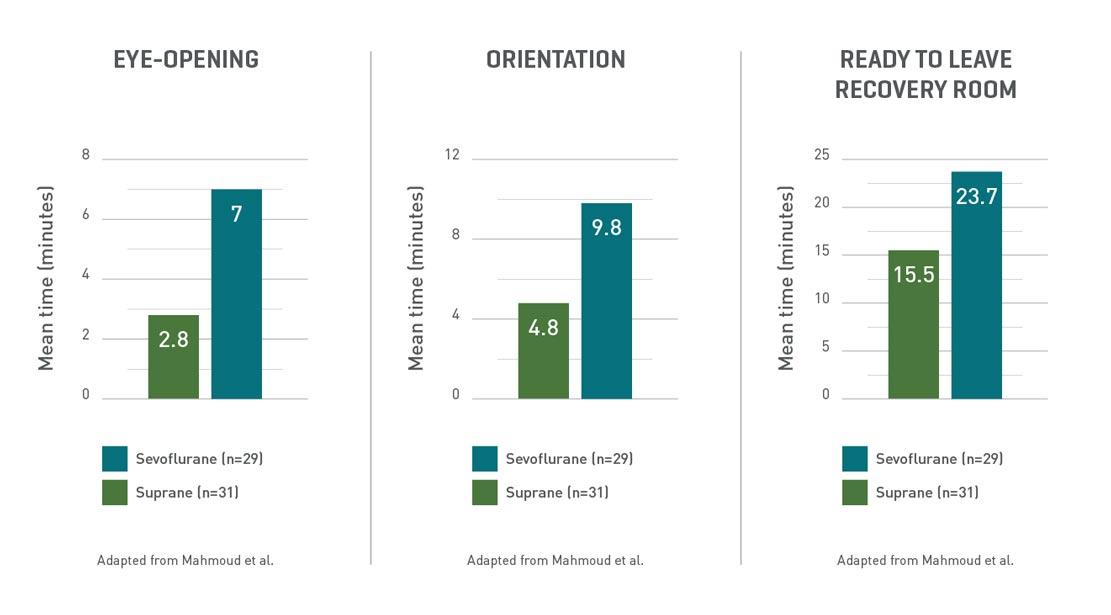
In a study of maintenance anaesthesia in 60 patients undergoing short day-case gynaecological surgery, 90% of day-case patients receiving Suprane returned to full ambulant activity the day following surgery, compared with 52% of patients receiving sevoflurane (p<0.01).12
Faster recovery without compromises
No difference was reported between Suprane and svoflurane groups in sleep disturbance, discomfort, analgesic consumption, or appetite.12

Faster wash-in and wash-out
Suprane has half the solubility of sevoflurane and the fastest wash-in and wash-out of all current potent halogenated inhaled anaesthetic agents.1-3
Suited for next day recovery
Suprane may offer rapid recovery in the surgical suite in day-case surgery. All assessments of early recovery were significantly faster in the Suprane (desflurane) group, compared with sevoflurane (p<0.0001).12*
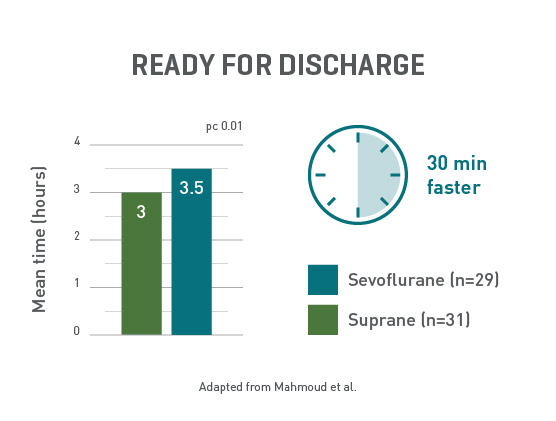
Ready to go home, faster
Day-case surgery patients receiving Suprane were ready for discharge at least 30 minutes faster than the sevoflurane group.12
Are you interested in additional information about Baxter Anesthesia?
*Maintenance anaesthesia with Suprane was initially 2−6%, and sevoflurane was initially 0.5−2.0% in oxygen/nitrous oxide in 60 gynaecological day-case patients aged 16−75 years (ASA I−II). The gases were given by laryngeal mask airway, with the vapour concentrations adjusted to meet the surgical requirements. Induction was with intravenous metoclopramide, fentanyl, and propofol. Mean duration of maintenance anaesthesia was 18 minutes in each group. Mean end-tidal vapour pressure at 5 and 10 minutes after induction was 4.5% for Suprane and 1.7% for sevoflurane, indicating that approximately equipotent concentrations of the two agents were given. Blood pressure and pulse rate at these times were similar in both groups.12
Important safety information
Eger EI, et al. The Pharmacology of Inhaled Anesthetics. Seminars in anesthesia, perioperative medicine and pain. 2002: 24(2);8-49.
Jakobsson J. Desflurane: A clinical update of a third‐generation inhaled anaesthetic. Acta anaesthesiologica scandinavica, 2012:(56)4;420-432.
Chudasama PA,et al. Comparison of haemodynamic parameters and recovery characteristics between sevoflurane and desflurane in patients undergoing day-care surgical procedure. Adv Hum Biol 2018; 8: 140-4.
Nathanson MH, et al. Sevoflurane versus desflurane for outpatient anesthesia: a comparison of maintenance and recovery profiles. Anesth Analg 1995; 81: 1186-90.
Yasuda N et al. Kinetics of desflurane, isoflurane, and halothane in humans. Anesth. 1991;74(3):489-498.
McKay RE, et al. Effect of increased body mass index and anaesthetic duration on recovery of protective airway reflexes after sevoflurane vs desflurane. Br J Anaesth. 2010:104(2);175-82.
Dupont J, et al. Recovery after anaesthesia for pulmonary surgery: desflurane, sevoflurane and isoflurane. Br J Anaesth. 1999;82(3):355-359.
Heavner JE, et al. Recovery of elderly patients from two or more hours of Desflurane or Sevoflurane anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 2003; 91:502-6.
Magni G, et al. A comparison between sevoflurane and desflurane anesthesia in patients undergoing craniotomy for supratentorial intracranial surgery. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2009;109(2):567-71.
Erk G, et al. Anesthesia for laparoscopic cholecystectomy: comparative evaluation—desflurane/sevoflurane vs. propofol. Middle East Journal of Anaesthesiology, 2007;19(3):553-562.
La Colla L et al. Faster wash-out and recovery for desflurane vs sevoflurane in morbidly obese patients when no premedication is used. Br J Anaesth. 2007;99(3):353-358
Mahmoud NA, et al. Desflurane or sevoflurane for gynaecological day-case anaesthesia with spontaneous respiration? Anaesth. 2001;56(2):171-174.
Bilotta F, et al. Early postoperative cognitive recovery and gas exchange patterns after balanced anesthesia with sevoflurane or desflurane in overweight and obese patients undergoing craniotomy: a prospective randomized trial. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2009;21(3):207-213.
Caverni V, et al. Hypotensive anesthesia and recovery of cognitive function in long-term craniofacial surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2005;16(4):531-536.
Juvin P, et al. Emergence of elderly patients from prolonged desflurane, isoflurane, or propofol anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 1997;85(3):647-651.
Gupta A, et al. Comparison of recovery profile after ambulatory anesthesia with propofol, isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane: a systematic review. Anesth Analg. 2004;98(3):632-641.
Beaussier M, et al. Haemodynamic stability during moderate hypotensive anaesthesia for spinal surgery. A comparison between desflurane and isoflurane. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2000;44(9):1154-1159.
Landoni G, et al. Desflurane and sevoflurane in cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Journal of cardiothoracic and vascular anesthesia. 20071;21(4):502-11.
Baily JM. Context-sensitive half-times and other decrement times of inhaled anesthetics. Anesth Analg. 1997 Sep: 85(3): 681-6.
Liu et al. Postoperative recovery after anesthesia in morbidly obese patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Can J Anaesth. 2015: 62(8) 907-17.
Chen G, et al. Comparison of early recovery and cognitive function after desflurane and sevoflurane anaesthesia in elderly patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of International Medical Research. 2015;43(5):619-28.
Uhlig C, et al. Effects of Volatile Anesthetics on Mortality and Postoperative Pulmonary and Other Complications in Patients Undergoing Surgery. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Anesthesiology: The Journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists. 2016;124(6):1230-45.
Grottke O, et al. Intraoperative wake-up test and postoperative emergence in patients undergoing spinal surgery: a comparison of intravenous and inhaled anesthetic techniques using short-acting anesthetics. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2004;99(5):1521-7.
Gökçek E, et al. Early postoperative recovery after intracranial surgical procedures. Comparison of the effects of sevoflurane and desflurane. Acta cirurgica brasileira. 2016;31(9):638-44.
Mckay RE, et al. Airway reflexes return more rapidly after desflurane anesthesia than after sevoflurane anesthesia. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2005;100(3):697-700.
De Oliveira Jr GS, et al. Desflurane/fentanyl compared with sevoflurane/fentanyl on awakening and quality of recovery in outpatient surgery using a laryngeal mask airway: a randomized, double-blinded controlled trial. Journal of clinical anesthesia. 2013;25(8):651-8.
Pin-On P, et al. Desflurane is not inferior to sevoflurane in the occurrence of adverse respiratory events during laryngeal mask airway anesthesia: a noninferiority randomized double-blinded controlled study. Minerva Anestesiologica. 2020;86(6):608-616.
Dalal KS, et al. Desflurane for ambulatory anaesthesia: A comparison with sevoflurane for recovery profile and airway responses. Indian journal of anaesthesia. 2017;61(4):315.
Fanelli G, et al. Fast-track anaesthesia for laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a prospective, randomized, multicentre, blind comparison of Desflurane-Remifentanil or Sevoflurane-Remifentanil. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2006;23:861-8.
Gangakhedkar GR, et al. A prospective randomized double blind study to compare the early recovery profiles of desflurane and sevoflurane in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2019;35:53-7.
Bonanni A, et al. Volatile Anesthetics versus Propofol for Cardiac Surgery with Cardiopulmonary Bypass, Meta-analysis of Randomized Trials. Anesthesiology. 2020;132(6):1429–1446
This site is only intended for HCP professionals.
This site is intended for Healthcare Professionals. Your website experience will be determined by your selection and regulatory-approved product information.
If you are not a Healthcare Professional, please visit www.Baxter.com